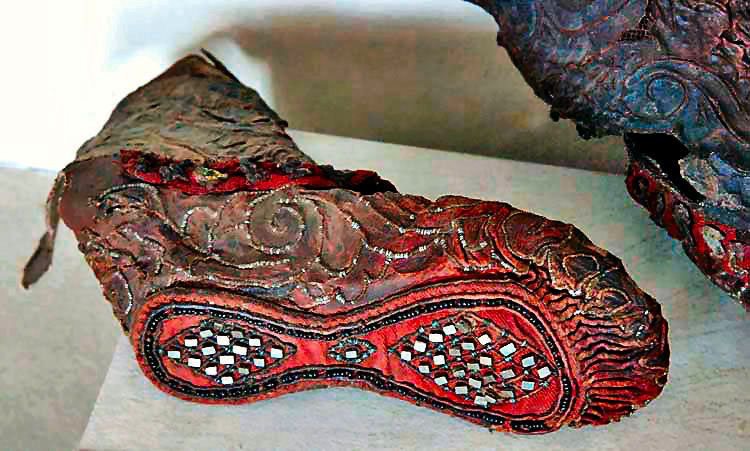

The allure of ancient artifacts has intrigued historians and art historians alike, but rarely do archaeologists come across age-old remnants that have survived thousands of years in near-mint condition. In 1948, a women's boot, featuring intricately bedazzled patterns, was discovered in Siberia's Altai mountains alongside other important finds—including jewelry, food, and weapons. This stunning shoe is believed to be 2,300 years old and features an elaborate sole made up of soft red leather and a geometric design sewn with pyrite crystals and black beads.
Ancient Scythians were a nomadic people who traversed the Eurasian continent. The shoe's location in the Altai Mountains is thought to be one of the Scythian's burial mounds, which accounts for many other objects and clothing found near the boot. Like other ancient civilizations, it was customary for these nomads to bury their dead with essentials to help them travel to the afterlife. Scythians typically constructed wooden cabin-like structures deep in the ground to house their dead, where each body was placed inside a log coffin filled with their possessions. This scrupulous preparation together with the permafrost of the Altai Mountains preserved the boot for centuries.
The exquisite beading on the sole of the leather shoe has sparked a great deal of curiosity and speculation online. According to historians, Scythians often socialized in front of a fire while sitting on their knees, so the detailing on the bottom of the shoes would be visible to others, and thus an important aspect of a person's attire. Some theorists propose that the boot was made exclusively for burial, which would account for the immaculate state of the sole.
This spectacular shoe is now part of the State Hermitage Museum‘s collection of ancient artifacts in St. Petersburg, Russia.
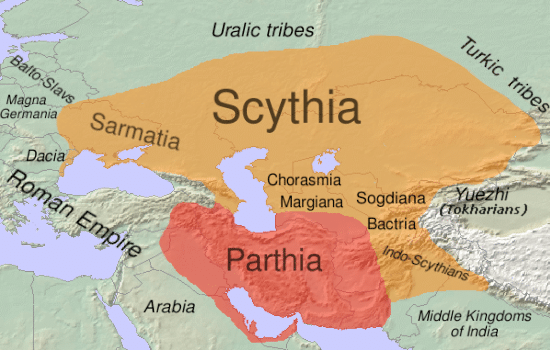
Approximate extent of Scythia in 1st century BCE
Fossilized skin of Paleozoic reptile estimated to be 286 to 289 million years old based on stalagmite rings from a nearby limestone cave, predating dinosaurs by nearly 50 million years.